Mortgage Rates Dip to 6.32% Amid Economic Uncertainty and Housing Challenges
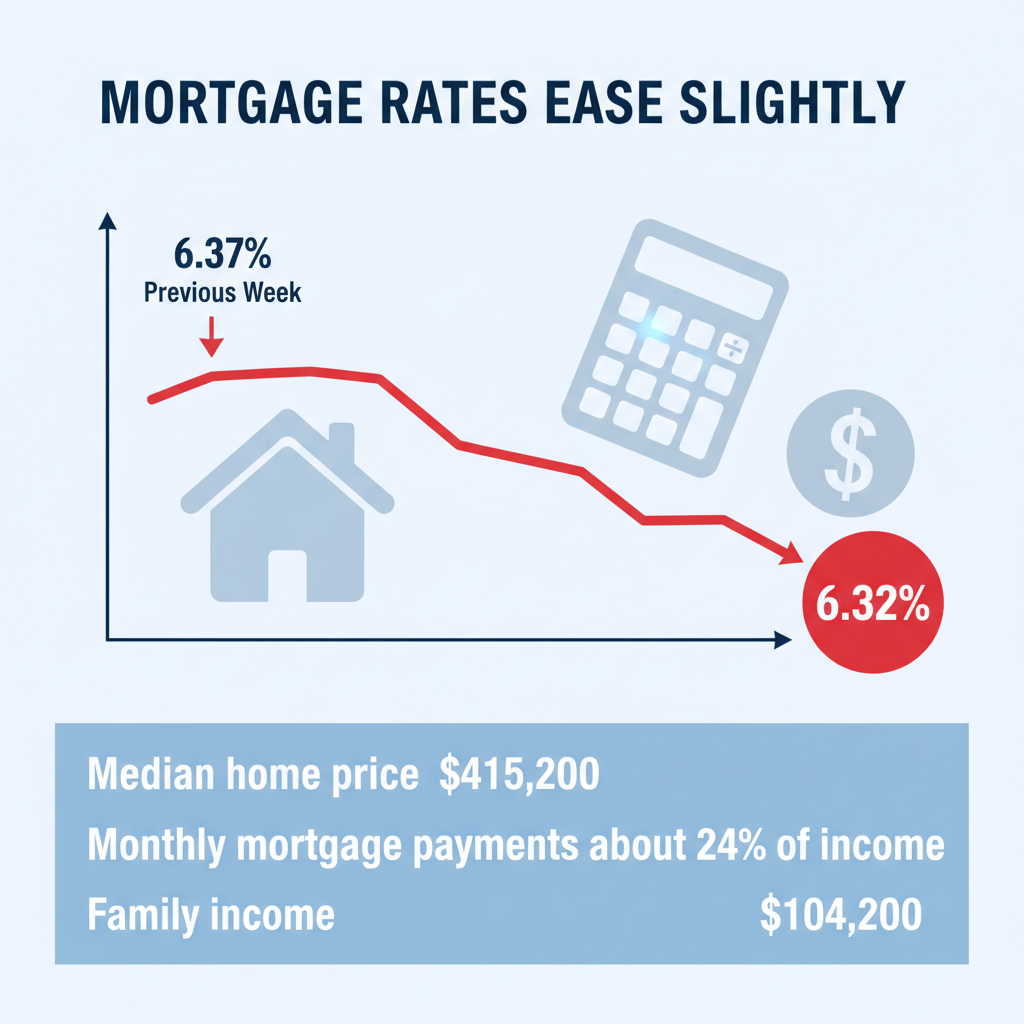
Mortgage rates dipped slightly this week, with the 30-year fixed rate averaging 6.32%, down from 6.37% the previous week, according to Bankrate’s latest survey.
Despite this decrease, rates remain high compared to previous years amid economic challenges like inflation and a slowing job market.
Monthly mortgage payments now consume about 24% of average family income based on 2025 projections.
Proposals for 50-year mortgage terms face criticism due to concerns over higher costs and delayed equity-building.
The housing affordability crisis is largely driven by supply shortages rather than mortgage term changes.
Summary

Mortgage rates dipped this week, with the 30-year fixed rate averaging 6.32%, down from 6.37% the previous week, according to Bankrate’s latest lender survey.
Mortgage rates in the United States have experienced a slight decrease this week, offering a glimmer of hope to prospective homebuyers and those considering refinancing. Despite this modest dip, rates remain elevated compared to previous years, influenced by economic policy decisions, market volatility, and broader economic challenges including inflation and a slowing job market. The housing affordability crisis continues to be shaped primarily by supply and demand dynamics rather than mortgage term length adjustments recently proposed by political figures.
- The 30-year fixed mortgage rate fell to an average of 6.32% this week, down from 6.37% the prior week.
- Median home prices and family incomes for 2025 indicate monthly mortgage payments equal about 24% of typical family income.
- The Federal Reserve’s recent interest rate cuts and market uncertainty continue to influence mortgage rates.
- Mortgage application volumes have dropped due to rising rates but remain higher than last year’s levels.
- Proposals for 50-year mortgage terms face criticism amid concerns about increased costs and housing affordability.
Current state of mortgage rates
According to Bankrate’s latest lender survey, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed mortgage has slightly declined to 6.32%, compared to 6.37% the previous week. This small adjustment is part of a broader trend where rates have fluctuated through late 2024 and 2025 after rising sharply from around 6.20% in early October last year. The 15-year fixed and 30-year jumbo mortgage rates similarly show minor decreases, though the rates remain elevated compared to historical averages.
Mortgage loans typically include discount and origination points, which can affect the overall interest costs consumers pay. On average, this week’s 30-year fixed mortgages contained 0.32 points, representing combined fees aimed at reducing rates or covering lender costs.
Affordability and monthly payments
The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development projects the national median family income for 2025 to be approximately $104,200. Meanwhile, the National Association of Realtors reports a median sale price for existing homes in October 2025 of $415,200. With a common 20% down payment and a 6.32% mortgage rate, monthly mortgage payments are estimated at $2,060, which consumes about 24% of the average family’s monthly income.
Samir Dedhia, CEO of One Real Mortgage, highlights that increased home inventory and stabilizing prices create promising conditions for buyers and refinancers despite potential volatility heading into year-end Federal Reserve meetings.
Federal Reserve actions and economic outlook
The Federal Reserve trimmed its benchmark interest rate twice in 2025 but opted to maintain the federal funds rate steady through most of the year. Jerome Powell, Fed Chairman, took actions in September and October signaling cautious adjustments amid economic uncertainty. Importantly, fixed mortgage rates are influenced more by investor demand for 10-year Treasury bonds than by Fed policy alone. Market uncertainty typically prompts investors to buy Treasury bonds, lowering yields and indirectly reducing mortgage rates.
Despite these measures, economic growth shows signs of slowing. Inflation edged up to 3% in September 2025, stubbornly above the Fed’s 2% target, and the job market has exhibited weakening trends. President Donald Trump's tariff policies have been linked to inflationary pressures. The 10-year Treasury yield fluctuated around 4%, decreasing slightly over the past week.
Market fluctuations and refinancing considerations
Recent data from NerdWallet and Zillow confirm mortgage rates have edged down modestly, with the average 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at around 6.05% APR, slightly lower than the previous week. Although changes are incremental, this could encourage potential buyers or refinancers to monitor rate trends more closely.
Refinancing decisions are typically worthwhile if current rates offer at least a 0.5 to 0.75 percentage point reduction from existing loans. Homeowners with mortgage rates above approximately 6.55% may benefit from refinancing, depending on individual financial goals such as lowering monthly payments, shortening loan terms, or tapping home equity.
Buying a home in today’s market
For prospective buyers, timing the market perfectly is challenging. The essential factor is whether the buyer can afford a mortgage at current rates. Lower rates may emerge later, but refinancing remains an available strategy. Financial advisors recommend obtaining preapproval, shopping lender offers, and understanding budget constraints.
Tools like NerdWallet’s affordability calculator assist buyers in estimating payments. For those not yet ready to purchase, strengthening their financial profile by reducing debt and saving for down payments can lead to better loan conditions and rates when the time comes.
Locking mortgage rates and quote variability
Mortgage rate locking offers protection against rising rates during the loan approval process. Some lenders also provide float-down options, allowing borrowers to benefit if rates drop after locking. Given daily and even hourly rate volatility, locking a favorable quote can offer peace of mind.
It is important to note that published mortgage rates typically reflect “sample” rates for borrowers with optimal credit and large down payments, often including mortgage points. Individual quotes vary significantly based on credit scores, debt-to-income ratios, employment history, loan amounts, property type, and location.
Rising mortgage rates and application volumes
Recent weeks saw a three-week increase in mortgage rates to around 6.37%, prompting a decline in mortgage applications by 5.2%. Refinance applications fell 7% but remain substantially higher than the previous year, reflecting historic lows in refinancing activity then. Purchase applications declined slightly, though levels are up 26% year-over-year.
Analysts note that buyers are cautious amid fluctuating rates, although some segments, like FHA purchase applications, have seen small increases.
Political proposals and housing affordability
In early November 2025, President Donald Trump proposed introducing 50-year mortgage terms. While some, including Federal Housing Finance Agency Director Bill Pulte, praised this as transformational, many experts and political figures expressed reservations.
Extended mortgage terms could lower monthly payments—for instance, lowering a payment by approximately $340 on a $500,000 loan—but typically come with higher interest rates due to increased lender risks. Moreover, longer terms delay building homeowner equity, potentially leading to negative equity situations. Research from the 2000s subprime crisis shows underwater homeowners are significantly more likely to default.
Critically, experts agree that extending mortgage duration will not solve the housing affordability crisis, which is primarily driven by chronic underbuilding and a severe shortage of available homes. Since the housing market collapse over a decade ago, residential construction has remained insufficient to meet demand, leaving the U.S. in need of millions of additional housing units across all demographics.
Conclusion
While mortgage rates have slightly dipped, remaining near 6.3% for 30-year fixed loans, economic and political developments continue to impact the housing market significantly. Prospective buyers and refinancers are advised to remain vigilant, evaluate personal financial situations carefully, and take advantage of current conditions while preparing for inevitable market fluctuations. Meanwhile, addressing the broader supply constraints remains essential to achieving long-term housing affordability.
Questions and answers
Q: Current mortgage rates in the US
A: As of mid-2024, current mortgage rates in the US typically range between 6% and 7% for a 30-year fixed loan, though they can vary depending on the lender, borrower’s credit score, and loan type. Rates have fluctuated due to economic factors like inflation and Federal Reserve policies. It’s important for borrowers to shop around and check daily updates from financial news or lenders for the most accurate rates.
Q: Impact of Federal Reserve on mortgage rates
A: The Federal Reserve influences mortgage rates mainly through its control of short-term interest rates and its monetary policy stance. When the Fed raises or lowers its benchmark rates, mortgage rates generally follow the trend, though they are also affected by bond market conditions. A tighter monetary policy often leads to higher mortgage rates, making borrowing more expensive, while an easing policy tends to lower rates and stimulate home buying.
Q: How to refinance a mortgage
A: To refinance a mortgage, homeowners typically start by assessing their current loan terms and financial goals, such as lowering interest rates or changing loan duration. The next step is to shop around for lenders offering better terms and submit a refinancing application with necessary documentation like income verification and credit reports. Upon approval, the new loan pays off the existing mortgage, often resulting in updated payment terms that can save money or reduce monthly payments.
Q: Pros and cons of 50-year mortgage terms
A: A 50-year mortgage term offers lower monthly payments due to the extended repayment period, making it attractive for buyers seeking affordability. However, the cons include paying significantly more interest over the life of the loan and slower building of home equity. Additionally, longer terms can mean paying off the home much later in life, potentially affecting financial flexibility and retirement plans.
Q: Housing affordability and mortgage payments
A: Housing affordability is closely tied to mortgage payments, which depend on factors like home price, interest rates, loan term, and borrower income. When mortgage payments consume a large portion of income, it reduces affordability and can limit access to homeownership. Rising mortgage rates or home prices can strain budgets, making it essential for buyers to consider total monthly costs, including taxes and insurance, to ensure sustainable affordability.
Key Entities
Bankrate: Bankrate is a consumer financial services company that provides information on interest rates, mortgages, and personal finance. It recently reported on a survey regarding Americans' economic anxieties amid Federal Reserve policy changes.
Federal Reserve: The Federal Reserve is the central banking system of the United States responsible for setting monetary policy and regulating banks. It has implemented aggressive interest rate hikes to combat inflation, impacting Americans' financial confidence.
Samir Dedhia: Samir Dedhia is the founder and CEO of Bankrate. He commented on Americans' increasing economic anxieties following the Federal Reserve's rate hike decisions.
Jerome Powell: Jerome Powell is the Chair of the Federal Reserve, overseeing U.S. monetary policy. Under his leadership, the Fed has raised interest rates to address inflation concerns.
Donald Trump: Donald Trump is the former President of the United States who has criticized Federal Reserve policies. His political positions include opposing aggressive interest rate hikes implemented by the Fed.
External articles
- Lower Interest Rates Fail to Offset Effects of High Home ...
- California Housing Affordability Tracker (3rd Quarter 2025)
- Prospects for Improving Housing Affordability
Articles in same category
- Frontline (FRO) Valuation and Growth Amid Rising Oil Demand
- CRISPR Therapeutics Unveils Promising AATD Gene Editing Data
- Aston Martin Issues Profit Warning on Tariff Impact
YouTube Video
Title: End-of-2025 Mortgage Rates Hit 3-Year Lows
URL: https://www.youtube.com/shorts/5htZvQ_U3oo
Money