Impact of U.S. Tariffs on European Wine Exports and Transatlantic Trade Relations
Since August 2025, the United States increased tariffs on European wine and spirits from 10% to 15%, significantly impacting the EU’s major export sector to its largest overseas market. This tariff hike has led to higher prices for U.S. consumers, pressured importers’ profit margins, and strained the hospitality and retail industries reliant on European wine. European countries like France and Italy, along with industry groups such as the Comité Européen des Entreprises Vins (CEEV) and the U.S.-based Distilled Spirits Council, strongly oppose these tariffs, advocating for exemptions to ease financial pressures. The ongoing tariff dispute highlights broader uncertainties and tensions in U.S.-EU trade relations, complicating business planning and raising concerns about potential wider economic and diplomatic consequences.Summary
The Impact of U.S. Tariffs on European Union Wine Exports and Transatlantic Trade Relations
Since August 2025, the United States has imposed a 15% tariff on European wine and spirits, an increase from the previous 10% rate. This escalation significantly affects one of the European Union's largest export sectors, with the U.S. serving as the EU's largest overseas market, importing over €4.88 billion worth of wine annually. The tariff not only disrupts trade volumes and investments but also leads to increased prices for U.S. consumers and challenges for importers and related industries.
Economic Consequences for the Wine Sector and Associated Industries
The tariff hike imposes higher costs on American consumers, who face price increases for European wines. U.S. importers are pressured to either absorb these additional expenses or pass them on, affecting profit margins. The repercussions extend beyond producers and importers; the U.S. hospitality and retail industries—critical sectors that rely heavily on European wine—experience reduced demand and financial strain. Industry coalitions like "Toasts not Tariffs," which represents 57 U.S. associations, highlight the widespread adverse effects on transatlantic businesses, including American distributors and domestic winemakers who benefit from robust European wine imports.
European and Industry Opposition to Trade Barriers
Countries such as France and Italy, key players in the European wine market, have voiced strong opposition to the tariffs. The Comité Européen des Entreprises Vins (CEEV) has expressed deep disappointment over the failure to secure exemptions in the EU-U.S. trade framework negotiations. European stakeholders advocate for reinstating lower or zero Most Favoured Nation (MFN) tariffs for wines, seeking relief from the ongoing financial pressures.
Complementing European efforts, U.S.-based industry groups, including the Distilled Spirits Council, actively lobby the government to reconsider the tariffs. They emphasize the detrimental impact on approximately 1.7 million U.S. hospitality workers, stressing the importance of a swift resolution. Nevertheless, no carveouts for wine or spirits have been granted to date, illustrating the complexities and fragility of current trade negotiations.
Broader Implications for U.S.-EU Trade Relations
The tariff situation exemplifies the broader uncertainty and tension in U.S.-EU trade relations. The absence of a comprehensive, legally binding agreement leaves exporters and importers uncertain, complicating strategic business planning and investment. Moreover, the wine and spirits sector, owing to its economic significance and cultural resonance, has become a focal point in debates about the efficacy of tariff-based trade policies. The situation raises concerns about the potential for wider economic and diplomatic consequences resulting from prolonged trade disputes.
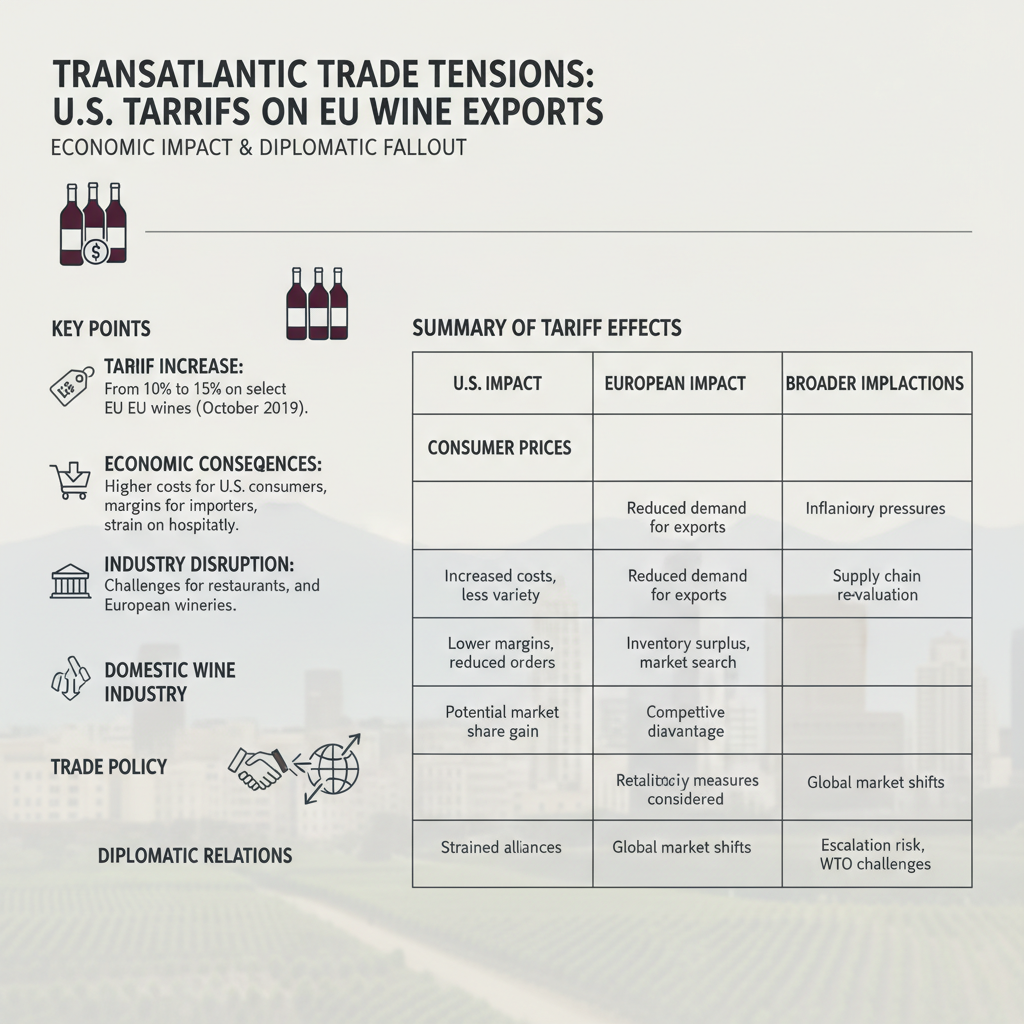
Summary of Key Tariff Effects
| Aspect | Impact in the U.S. | Impact in Europe | Broader Implications | |--------------------|-------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------| | Consumer Prices | Elevated prices for European wines | Reduced export competitiveness | Affects affordability and consumer choice | | Importers | Higher costs and reduced profit margins | Lower turnover and investment delays | Disrupts supply chains | | Domestic Wine Industry | Possible short-term benefits but long-term risks | N/A | Market instability and retaliation risk | | Trade Policy | Ongoing negotiations with no exemptions | Intense lobbying for carveouts | Reflects broader trade uncertainty | | Diplomatic Relations | Increased strain | Growing frustration and calls for resolution | Potential for wider economic and political fallout |
Conclusion
The 15% U.S. tariff on European wine and spirits deeply impacts the transatlantic trade landscape, raising challenges for European exporters, U.S. importers, consumers, and the hospitality sector. Despite concerted opposition from European countries, industry coalitions like CEEV and the Distilled Spirits Council, the absence of exemptions highlights the persistent complexities within U.S.-EU trade negotiations. This trade dispute underscores the broader risks associated with tariff-driven policies amid incomplete trade frameworks, emphasizing the need for diplomatic and economic solutions that support mutually beneficial trade relations.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: impact of U.S. tariffs on European wine
A: U.S. tariffs on European wine have increased the cost of importing these products into the United States, making European wines more expensive for American consumers. This has led to decreased sales and market share for European wine producers in the U.S., potentially shifting demand toward other competitors or domestic wines. Additionally, the tariffs strain trade relations and may prompt retaliatory measures, negatively impacting the broader wine industry and international trade dynamics.
Q: how tariffs affect U.S. wine industry
A: Tariffs imposed on U.S. wine by foreign countries increase the price of American wines in those markets, making them less competitive compared to local or other imported wines. This can lead to reduced export sales, hurting wineries' revenues and profitability. Additionally, tariffs may prompt producers to scale back production or shift focus to domestic sales, creating market disruptions. Overall, tariffs negatively impact the growth and international presence of the U.S. wine industry.
Q: wine and spirits tariff exemptions
A: Wine and spirits tariff exemptions refer to specific situations where import taxes or duties on alcoholic beverages are reduced or eliminated. These exemptions can apply under free trade agreements, special economic zones, or for certain quantities or types of wine and spirits. Governments may grant tariff exemptions to promote trade, reduce costs for consumers, or support local industries. It's important to check the relevant country's customs regulations to understand the applicable exemptions.
Q: cost of tariffs on wine imports
A: Tariffs on wine imports can significantly increase the price of foreign wines, making them more expensive for consumers. The exact cost varies depending on the country of origin, trade agreements, and the importing country's tariff rates. For example, tariffs can range from a few cents per liter to percentages that add 20% or more to the retail price. These tariffs affect both importers and consumers by reducing competitiveness and limiting access to a diverse range of wines.
Q: effects of trade policy on wine prices
A: Trade policies, such as tariffs, import quotas, and trade agreements, can significantly impact wine prices by altering the cost and availability of imported wines. Tariffs increase the cost of foreign wines, leading to higher prices for consumers, while trade agreements that reduce or eliminate tariffs can decrease prices and increase variety. Additionally, restrictions or standards imposed by trade policies can influence the competitiveness and market access of wine producers, further affecting price levels. Overall, trade policies directly shape the supply chain costs and market dynamics that determine wine prices.
Key Entities
France: France is a leading global producer of wine, renowned for its diverse terroirs and prestigious wine regions such as Bordeaux and Burgundy. It plays a significant role in the international wine trade and influences global wine standards.
Italy: Italy is one of the world's largest wine producers, with a rich heritage in viticulture and regions like Tuscany and Piedmont. Its wines are characterized by regional diversity and traditional grape varieties.
Washington: Washington State is a major wine-producing region in the United States, known for its high-quality red and white wines. The area benefits from a unique climate that contributes to the distinctive profile of its varietals.
U.S. Wine Trade Alliance: The U.S. Wine Trade Alliance is an organization that advocates for American wine producers and facilitates trade relationships. It aims to enhance market access and promote U.S. wines domestically and internationally.
V.O.S. Selections: V.O.S. Selections is a wine importer specializing in sourcing quality wines from Europe and distributing them in the U.S. market. The company focuses on representing distinctive producers to expand consumer choice.
External articles
- California wine industry torn on Trump tariffs
- U.S.-EU-UK Tariffs on Distilled Spirits and Wines
- Trump's tariffs give European wineries — and US importers
Related Articles
- Josetta Saffirio: Sustainable Barolo Wine Innovation in Piedmont
- 2022 Nicolas Jay Own-Rooted Pinot Noir: Terroir-Driven Oregon Wine
- Tenuta Stella Organic Wine 2023 Vintage: Sustainability and Innovation in Friuli
YouTube Video
Title: Trump Tariffs Are Hurting The Economy
URL: https://www.youtube.com/shorts/xm0go6oyWYQ
Dining