Effectiveness of Digital Learning: Comparing Reading and Listening for Better Retention
Digital learning involves various formats like reading texts and listening to audio content, each affecting comprehension and retention differently. Reading generally leads to better understanding and long-term retention due to visual reinforcement and self-paced study, while listening fosters emotional engagement but can be less effective for complex information. Combining both methods—known as dual modality learning—leverages their strengths, enhancing cognitive engagement and retention. Technology, such as text-to-speech and adjustable playback speeds, supports this integration, allowing learners to optimize their experience. Recognizing individual differences and the challenges of multitasking is crucial for tailoring effective digital learning strategies.
Summary
Understanding the Effectiveness of Digital Learning Through Reading and Listening
In today's digital learning environment, learners encounter diverse formats such as reading texts, listening to audiobooks, and engaging with podcasts. Each format impacts cognitive engagement, comprehension, and information retention differently. Recognizing how these modalities function individually and in combination is essential for optimizing learning.
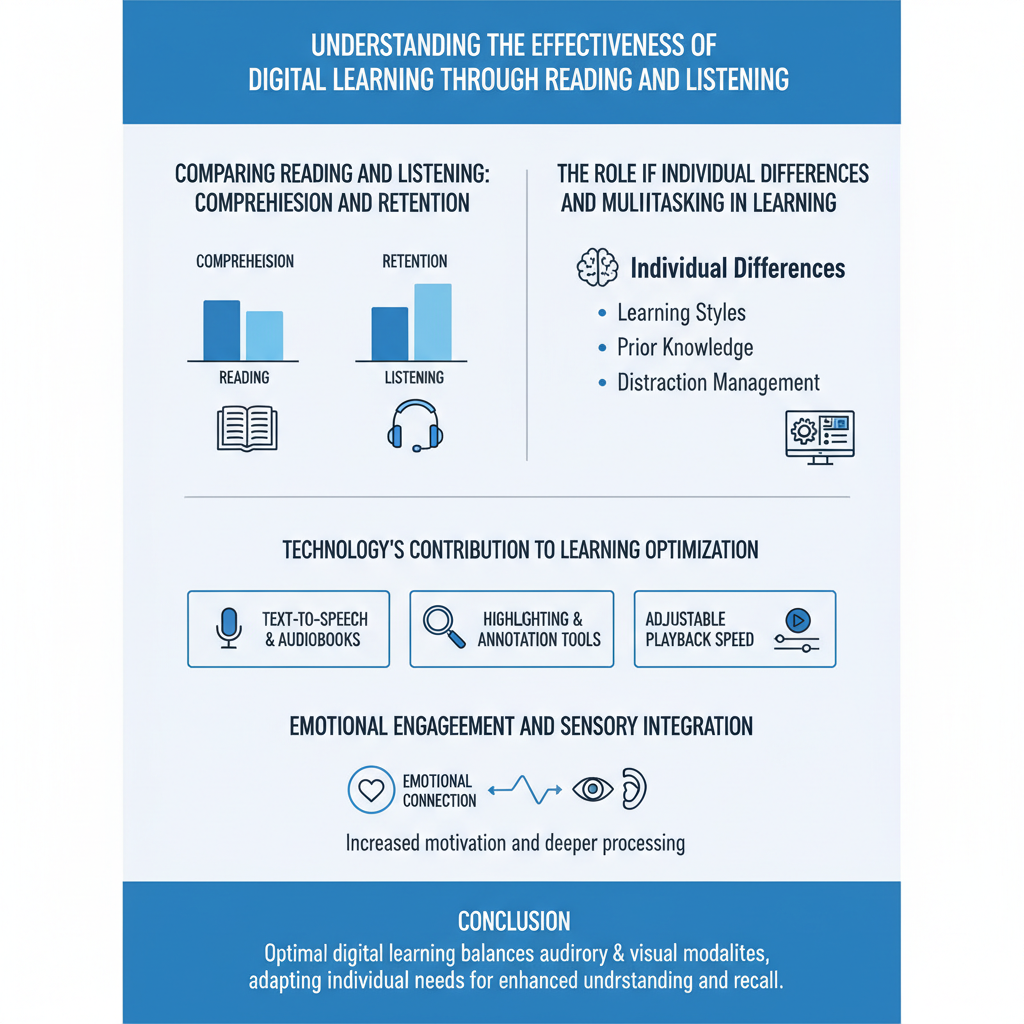
Comparing Reading and Listening: Comprehension and Retention
Studies consistently find that reading generally produces better comprehension and long-term retention compared to listening alone. This advantage arises primarily from the visual reinforcement reading offers and the learner’s control over pacing. Readers can pause, reread, and analyze complex material at their own speed, enhancing understanding and retention.
Conversely, listening relies on auditory processing and is often less effective for complex information. Factors such as speaker accent, speech rate, and background noise can hamper comprehension. However, listening can foster emotional engagement, providing empathetic connections to content that reading may not evoke as strongly. When combined with visual aids or text, listening can improve retention, especially in multitasking scenarios.
The Role of Individual Differences and Multitasking in Learning
Individual variations significantly influence how learners comprehend and retain information. Some individuals may benefit more from dual modality learning, combining reading and listening to engage multiple cognitive pathways simultaneously.
Multitasking presents notable challenges for both reading and listening. Divided attention reduces cognitive engagement, negatively impacting comprehension and information retention regardless of format. While listening might seem advantageous in multitasking environments, its effectiveness decreases without accompanying visual support or the ability to control playback pace.
Technology’s Contribution to Learning Optimization
Modern technology plays a key role in enhancing digital learning. Text-to-speech tools and playback adjustment features empower learners to control the pace of auditory content, partially mitigating the challenges of listening comprehension. Adjusting playback speed allows for revisiting critical sections and aligning audio delivery with individual processing rates.
Dual modality learning, where reading and listening occur simultaneously, leverages the strengths of both visual and auditory processing. This integration enhances cognitive engagement by stimulating different neural pathways, leading to improved comprehension and retention.
Emotional Engagement and Sensory Integration
Listening enhances emotional connection with learning material through auditory cues such as tone and inflection. This emotional engagement can increase motivation and interest. However, reading provides concrete visual reinforcement, enabling deeper cognitive engagement necessary for mastering complex subjects.
Combining both methods creates a balanced learning approach, integrating emotional resonance and cognitive rigor. Visual reinforcement supports understanding, while auditory input enriches emotional context.
Conclusion
The effectiveness of digital learning relies on understanding the strengths and limitations of reading and listening. Reading offers superior comprehension and retention through visual reinforcement and self-paced study, while listening enables emotional engagement and accessibility in multitasking contexts. Leveraging technology to control pace and combining both modalities enhances cognitive engagement and optimizes learning outcomes. Ultimately, tailoring learning strategies to individual needs and integrating dual modality approaches can improve the acquisition and retention of complex information.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do you learn more from reading or listening?
A: Whether you learn more from reading or listening depends on your personal learning style and the context. Reading allows you to process information at your own pace, review content easily, and focus on details, which benefits many learners. Listening, on the other hand, can be more effective for auditory learners and is useful for understanding tone and emphasis. Combining both methods often yields the best results, as it engages multiple senses and reinforces learning.
Q: Benefits of audiobooks vs reading books
A: Audiobooks offer convenience and multitasking opportunities, allowing listeners to enjoy books while commuting, exercising, or doing chores. They can enhance comprehension and retention for auditory learners and provide access to literature for individuals with visual impairments or reading difficulties. Reading physical books, on the other hand, can improve focus and reduce distractions, often enhancing critical thinking and memory retention. Both formats have unique advantages depending on personal preferences and situations.
Q: How does multitasking affect listening comprehension?
A: Multitasking can significantly impair listening comprehension because the brain has limited cognitive resources. When a person tries to perform multiple tasks simultaneously, especially those requiring attention, their ability to fully process and understand auditory information diminishes. This divided attention leads to reduced retention, increased misunderstanding, and less effective communication. Essentially, multitasking during listening makes it harder to focus, leading to poorer comprehension.
Q: Strategies to improve retention from audiobooks
A: To improve retention from audiobooks, actively engage with the content by taking notes or highlighting key points while listening. Listening in a distraction-free environment helps maintain focus. Repeating challenging sections or listening at a slower speed can enhance comprehension. Additionally, discussing the material with others or summarizing what you’ve learned reinforces memory and understanding.
Q: Is reading better for learning science topics?
A: Reading is an effective way to learn science topics because it allows you to absorb detailed information, review concepts at your own pace, and revisit complex ideas as needed. However, combining reading with other methods like hands-on experiments, visual aids, and discussions can enhance understanding and retention. Different learning styles mean that while reading is beneficial for many, supplementing it with active learning approaches often leads to better comprehension of science subjects.
Key Entities
Marte Pupe Støyva: Marte Pupe Støyva is prominently featured in the context of the article, likely contributing to or leading the discussed initiative. Her role connects academic insights with practical applications relevant to the institutions mentioned.
Vivian Kjelland: Vivian Kjelland is associated with the thematic focus of the article, possibly as a researcher or expert. Her involvement suggests a contribution to the academic or media-based discussions outlined.
University of Stavanger: The University of Stavanger is a Norwegian institution known for research and education in technology, humanities, and social sciences. It features in the article as part of collaborative academic efforts or research initiatives.
University of Agder: The University of Agder is a Norwegian public university that offers diverse programs and engages in research across various disciplines. Its mention indicates participation in the academic or media projects described in the article.
Bauer Media: Bauer Media is a European media company operating numerous radio stations, digital platforms, and print publications. It is referenced in connection with media dissemination or collaboration within the article's scope.
External articles
- Do You Really Need to Read to Learn?
- Reading rate and most efficient listening rate are highly ...
- Does Reading while Listening to Text Improve ...
Articles in same category
- Victoria’s Secret Brand Identity Crisis and Shift to Inclusivity
- Assessing Donald Trump's Prospects for the Nobel Peace Prize: Independence, Criteria, and Controversies
- Rising Interest in Norwegian Language and Culture Among Young Americans
YouTube Video
Title: Do Audiobooks Count As Reading?
Channel: vlogbrothers
URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=80SCl6n0TEo
Published: 9 months ago
Life